A “Service All-Wheel Drive System” alert signals a problem with the all-wheel drive mechanism. This could stem from something as simple as fitting the wrong tire size or a weak battery. Additionally, degraded or contaminated fluid in the rear differential, a malfunctioning control module, or corroded connectors might be to blame.
Understanding the All-Wheel Drive System and Its Warning
The all-wheel drive (AWD) system distributes engine power across all four wheels to enhance traction. It employs a driveshaft to allocate power between the front and rear axles, ensuring better grip on various surfaces.
When the “Service All-Wheel Drive System” warning appears, the AWD system is deactivated, leaving only the front wheels to drive the vehicle.
This warning may remain constant or blink periodically, often accompanied by an audible beep. While prevalent in General Motors vehicles, it can occur in other makes as well.
Reasons Behind the ‘Service All-Wheel Drive System’ Alert and Fixes
The AWD warning frequently arises due to issues with the rear differential. However, other components’ failures can also activate this alert.
Weak Battery
Begin troubleshooting by checking the battery’s charge when the AWD warning lights up. The AWD system depends on sufficient battery power to function. If the voltage falls below 9 volts, the system shuts off the rear wheels and displays the warning to notify the driver.
A system diagnostic scan revealing a C0550 error code confirms a low or faulty battery as the cause. This code may appear as a stored or pending diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Addressing this issue is straightforward. Replace a defective battery to resolve the problem. If the battery is still functional, inspect the electrical system for a parasitic drain that could be depleting it.

Tire Issues
Even a minor issue like incorrect tire size can trigger the AWD warning. Using tires of different sizes or replacing only one or two tires instead of all four can confuse the traction control system, leading to uneven wear on the drivetrain components.
This mismatch prompts the AWD system to display the warning. To prevent this, always use the correct tire size and replace all four tires simultaneously to maintain consistency in the traction control system.

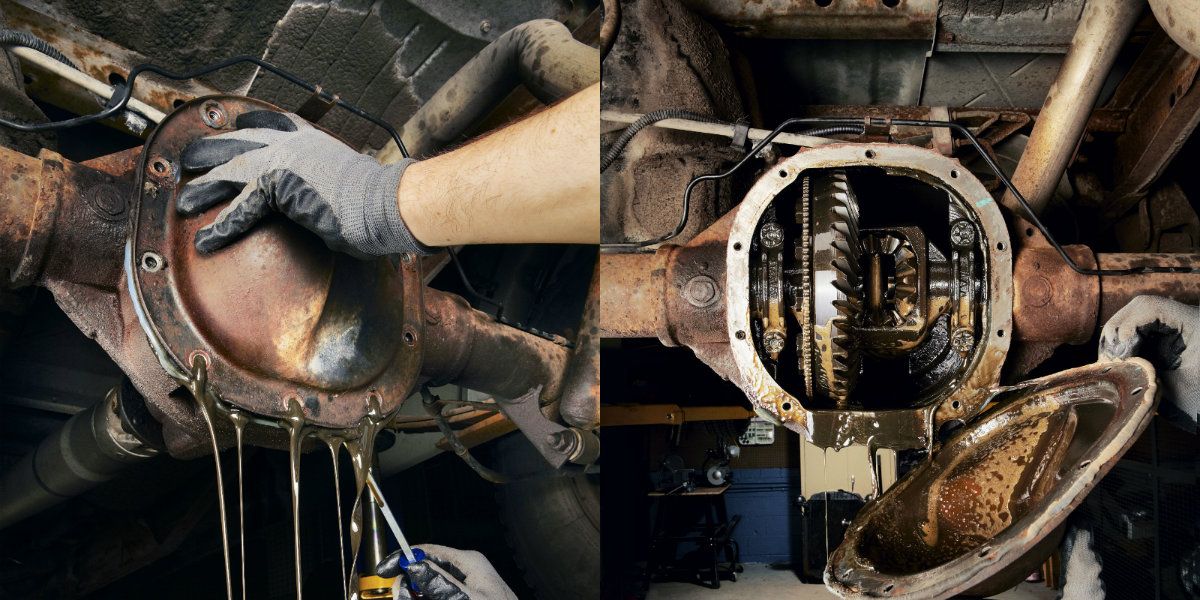
Corroded Electrical Connectors
Corrosion in the rear differential harness or control module connector can activate the AWD warning. The rear differential’s control module manages its operations, and the harness connects to this module.
Water exposure can cause corrosion in these connectors, gradually damaging the pins and disrupting electrical connections.
This disruption triggers the AWD warning. Applying dielectric grease to the connectors can prevent corrosion. If corrosion has already set in, replacing the affected connectors is necessary.
Defective Control Module
A faulty control module can also cause the AWD warning to appear. Exposure to moisture can short-circuit the module, rendering it inoperative.
If the control module gets wet, clean it immediately and apply dielectric grease to protect it. If the module is already damaged, replacement is the only solution.
Overheated Clutch Assembly
An overheated rear differential clutch assembly can also prompt the warning. This assembly transfers torque to the rear axle and includes a sensor monitoring its temperature, which should stay between -40°C and +120°C.
If the clutch assembly overheats, the AWD system disables the rear wheels, triggering the dashboard warning. Once the temperature returns to normal, the rear wheels reactivate, and the warning typically disappears after a few drive cycles.
Contaminated Differential Fluid
The rear differential consists of the clutch assembly and the ring gear, separated by a seal to keep their respective fluids from mixing.
General Motors advises replacing these fluids every 150,000 miles. Dirty or contaminated fluid due to prolonged use can trigger the AWD warning.
A failed seal can also allow the fluids to mix, impairing the rear differential’s operation and activating the warning. Regular fluid replacement at the recommended intervals prevents these issues, and a failed seal must be replaced.

Addressing the ‘Service All-Wheel Drive System’ Warning
When the AWD warning appears, use a diagnostic scan to identify error codes and pinpoint the issue. A standard OBD scanner may not detect AWD-specific trouble codes, so a scanner compatible with the AWD system is required.
Once the cause is identified, you can address it. However, AWD system repairs can be complex, even for experienced DIYers. Consulting a professional mechanic is advisable to avoid further damage.
Conclusion
When the AWD warning appears, the vehicle switches to front-wheel drive. Issues with the rear differential system are common culprits, but factors like incorrect tire sizes or a weak battery can also trigger the alert.