Comparing the Fuel car with their formidable opponent electric cars is no easy task. Understanding the difference in design between fuel cars and electric cars would give us enough insight as to why electric cars are faster than fuel cars.
When you shop for a new car, aside from the build of the vehicle, you’re most likely going to be interested in one thing – speed. This feature has fascinated car lovers all over the world and has even led to the development of car racing competitions around the world.
Why have Electric Vehicles become so popular for their speed? Are they lighter than fuel cars? Do they have a special kind of engine that propels them? Join me in investigating the hype surrounding the speed of electric vehicles.
What are Electric Cars?

Electric cars (EVs), often known as battery electric vehicles, are powered by an electric motor rather than an internal combustion engine.
The electric motor is powered by a huge traction battery pack, which must be hooked into a wall outlet or charging station, commonly known as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE).
One advantage of the EVs being powered by electricity is that there is no emissions from the tailpipe, and no normal liquid fuel components such as a fuel pump, fuel line, or fuel tank are present.
Major components of the Electric cars
- Battery: The battery is the source of power that provides electricity to the Evs parts.
- Charge port: This is the part you plugin the dedicated charger of your vehicle to charge the battery pack.
- Power electronics controller: This system regulates the flow of electricity coming from the battery pack and regulates the speed of the electric motor and torque generated by the motor.
- Thermal system (cooling): This unit maintains the optimum operating temperature of the vehicle.
- Transmission (electric): Similar to that of the fuel car, it transmits the power generated from the torques to the wheels.
- Onboard charger: This circuit converts electricity from AC into DC. It also communicates with other accessories such as the charging equipment and keeps a tab of the voltage, current, etc.
- DC/DC converter: converts the high voltage of DC power to lower Dc power.
What Are Fuel Cars?

Gasoline and diesel vehicles are similar. They both use internal combustion engines. A gasoline car typically uses a spark-ignited internal combustion engine rather than the compression-ignited systems used in diesel vehicles.
The fuel is injected into the combustion chamber and combined with air in a spark-ignited system. A spark from the spark plug ignites the air/fuel mixture.
Major components of the Fuel Cars
- Battery: The battery delivers power to the engine and vehicle electronics/accessories.
- Electronic control module (ECM): The ECM regulates the fuel mixture, ignition timing, and emissions system, as well as monitors vehicle operation, protects the engine from abuse, and detects and troubleshoots faults.
- Exhaust system: The exhaust system sends exhaust gases from the engine out of the tailpipe.
- Fuel injection system: This mechanism injects gasoline into the engine’s combustion chambers in preparation for ignition.
- Fuel pump: A fuel line pump transports gasoline from the tank to the engine’s fuel injection system.
- Fuel tank (gasoline): A tank onboard the vehicle that stores fuel needed by the engine.
- Internal combustion engine (spark-ignited): In this part of the engine, fuel is injected into a combustion chamber, where it is fused with air and ignited by a spark plug.
- Transmission: The gearbox is responsible for transferring mechanical power from the engine and/or electric traction motor to the wheels.
The technology of the Electric Car Vs. Fuel Car
We’d need to get into the core of both vehicles to understand how they operate and why one has pros over the other and vice versa.
How Electric Cars Work

Unlike regular vehicles, EVs utilize an Electric traction motor to generate power.
EVs exploit the basic operating principle of Motors. It utilizes magnetism and the natural interaction of electric and magnetic fields.
When an electrical circuit is closed, enabling electrons to travel along a wire, the electrons create an electromagnetic field with a north and a south pole. When this happens in the presence of another magnetic field, opposite poles attract, and similar poles repel.
When a current flows through a motor, the shaft under the force of electromagnetism begins to spin in the direction of the electromagnetic force.
The EV motor utilizes these attracting and repelling forces to rotate the shaft, transforming power into torque and eventually rotating the wheels by periodically switching the polarity (swapping the north and south poles) of one set of electromagnets.
That’s it, at least the basic principle behind it.
How Fuel Cars Work
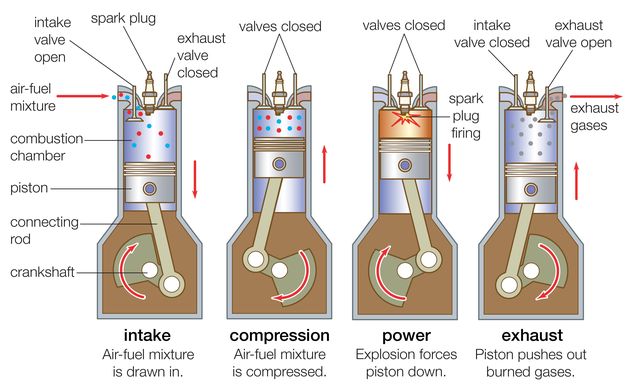
The operating principle is quite complex compared to EVs and would be too bothersome for the average car enthusiast. However, it is important to know that power is generated in the fuel car by means of combustion.
Internal-combustion engines are heat engines in the sense that they transform energy from the heat of burning gasoline into mechanical work or torque. To move the car, torque is delivered to the wheels.
In engines, a structure called a piston is installed inside metal tubes called cylinders( you’ve heard your mechanic mention this many times).
To simplify how the fuel works, we’d need a comparative analogy with the operus mandi of a bicycle. When riding bicycles, you move the paddles up and down with your legs; to compare with the car, Your legs are the Pistons that rotate the engine’s crankshaft (another famous term). Upon being turned by the pistons, the crankshaft causes the wheels to move.
Where is the power coming from?
I told you this wasn’t going to be simple. But if you want to know what advantage the EVs have over the fuel cars, then I’m afraid you have to keep reading.
So, continuing with our bicycle analogy, we use energy from food to turn the paddles, but where is the energy to turn the piston of the car engine coming from?
Take a breath!
Okay, let’s continue. Controlled amounts of fuel from the fuel tank flow into the cylinder where it enters the combustion chamber, where it’s compressed (with air mixture), then ignited to create an explosive force.
The explosive force pushes the piston (the pedals in a bicycle) back to its former position, and the cycle continues. See, that wasn’t so hard, was it?
Major Difference between Electric Cars and Fuel Cars
The underlying difference between both categories of vehicles is the mode by which both obtain the power to rotate their motors.
Because Fuel cars rely on a complex process of power generation, they take considerably longer to accelerate when compared to Electric cars.
This is because electric motors are much simpler than internal combustion engines. As a result, EVs can deliver full torque — the force that propels the car forward — from zero kilometers, resulting in instant acceleration. Simply put, the Motors of the EVs can reach a high speed in seconds.
Traditional combustion engines, on the other hand, take longer to get engine-generated power to the wheels and may need to “run” higher to get maximum torque.
Traditional gasoline cars also have more moving elements, such as the transmission, which makes them less efficient.
Other minor differences would be;
- The weight of both vehicles vary tremendously, with the EVs being considerably lighter than their fuel counterparts
- No Engine means more space. Electric cars have empty bonnets, which can now serve as a trunk.
- Since an EV doesn’t run on fuel, it is less likely to explode. EVs are known to burst into flames without an explosion.
- Less carbon emission by EVs compared to gas-powered cars
- Evs do not need frequent maintenance, making them manageable.
- Evs take longer to replenish energy, taking up to 8 hours to charge with a regular 200-400v charger.
- Evs are luxurious vehicles and quite expensive.
MUST READ: Can Electric Cars be Cheap and Fast? List of fastest Electric cars below 100K?
Can Electric cars Travel longer distances?
Of recent, People have been worried about the distance range of electric cars. However, most electric cars can travel much farther than fuel vehicles.
Fuel-powered cars (average cars) can reach up to 482 km on a full tank, while on a single charge, most electric vehicles have a range of 200-490 kilometers (124-304 miles).
According to the survey, newer EV vehicles such as the Hyundai Kona Electric (484 km), Chevrolet Bolt EV (459 km), and Kia e-Niro (455 km) currently have ranges comparable to a typical fuel car.
The Tesla Model S Long-Range can travel up to 610 km on a single charge, that’s almost 50% more than the average fuel car.
To put this incomprehensible context, you could easily drive from Brussels to Paris (316 km) or from London to Liverpool (350 km) without stopping for charging.
If you’re worried about how long the EVs battery would last, then you should know that the average car user travels for a distance of 40 -90km. So the EVs would not have any difficulty lasting you throughout the day. Unless, of course, you’re an uber driver who travels intra-states. Haha.
Can You Wait 8 Hours to Charge?
A major setback of Electric self-driving cars is the charging time. It could take almost 8 hours to charge a battery-dead EV. However, some stations offer fast-charging ports which can charge your batteries in 90 minutes or less.
However, unlike fuel cars, you don’t always need to make yourself present at the filling station to get a refill. EVs can be charged at home, and it is recommended you charge at night when you’re not going to use the car.
Comparing the Fastest Fuel and Electric Cars
Many people connect power with the deep rumble of revving engines and mistake EVs’ stillness for lack of speed and performance. In reality, the inverse is true. EVs accelerate quicker than gasoline-powered vehicles and have more than adequate speed for daily use.
The Rimac Nevera- All electric – speed 258 mph
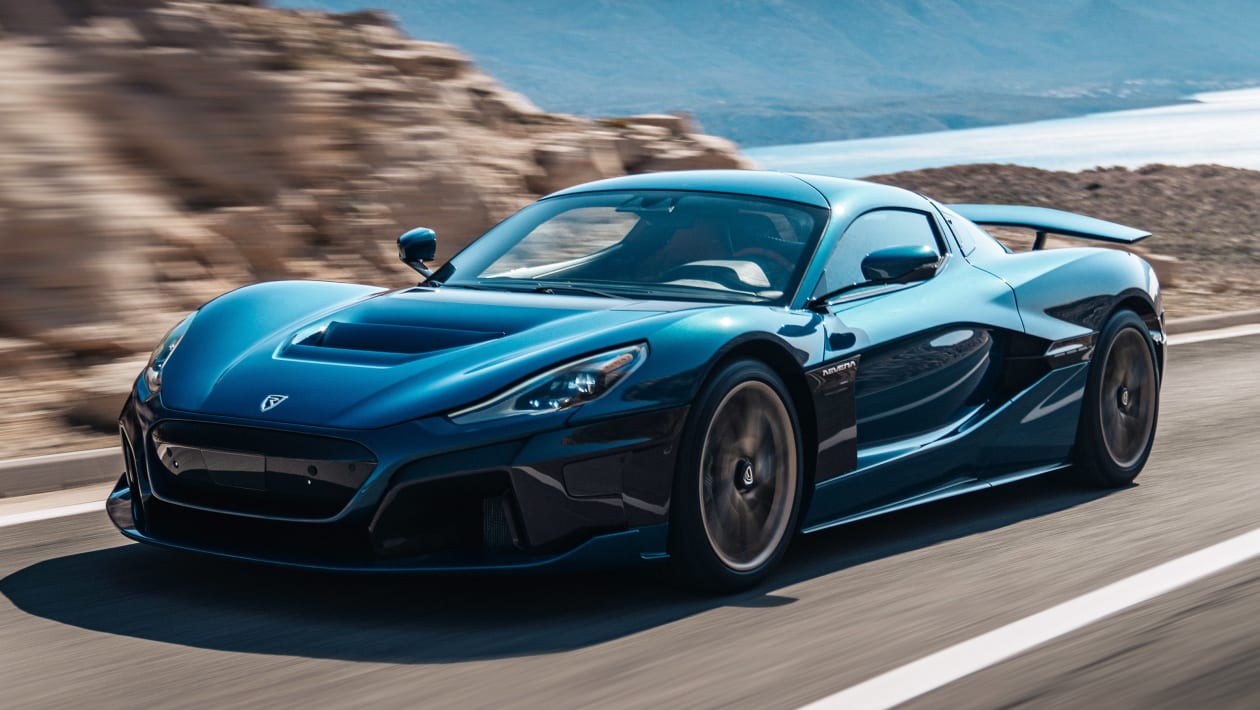

The Rimac Nevera is an electric sports automobile created and built by the Croatian automaker Rimac Automobili.
The Nevera is said to be capable of accelerating from 0 to 97 km/h (0 to 60 mph) in 1.85 seconds, making it perhaps the world’s fastest-accelerating production automobile.
It will go from 0–161 km/h (0–100 mph) in 4.3 seconds, 0–299 km/h (0–186 mph) in 9.3 seconds, and has a peak speed of 412 km/h, according to Rimac Automobili (256 mph).
Rimac claims the automobile was built to be extremely robust and capable of being driven aggressively. Furthermore, the automobile is technologically capable of Level 4 autonomous driving.
The Dodge Challenger SRT Demon
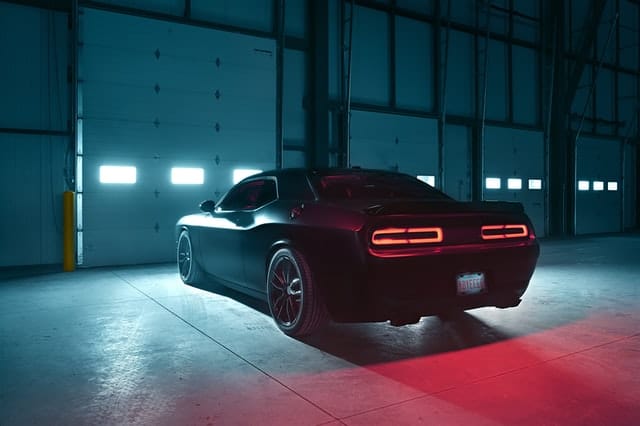

The 2018 Dodge Challenger SRT Demon is set to be the fastest and most powerful Challenger ever marketed to the general public.
This race-ready road vehicle maintains Dodge’s heritage of producing ever-more-muscular Challenger derivatives, such as the Hellcat. Only 3,000 of these drag-racing Challengers will be built for sale in the US.
When Dodge introduced the Challenger SRT Demon in 2018, it stated that the street-legal drag race car could reach a peak speed of 168 mph (270 km/h).
Since then, many others have attempted – and succeeded – in proving Dodge incorrect. The Demon’s highest speed was last reported to be greater than 203 mph (327 km/h) at the Johnny Bohmer Proving Grounds in Florida.
Which car is a Better Buy?
If the environment is important to you, get an EV because the initial high cost of purchasing will be offset in a few years. Also, if you live in a metro that has public charging stations or if you can build one at home, purchase one. However, it makes more sense to wait 2-3 years so that you have a larger selection of automobiles and a better charging station network.
According to a website located in the United States, EV batteries convert 59-62 percent of energy into vehicle movement, but gasoline-powered cars only convert 17-21 percent, making EVs more efficient. Furthermore, because there is no exhaust system, EVs are quiet and smooth, delivering a pleasant driving experience.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have learnt some basics with regard to how electric vehicles and fuel vehicles work. Different people may have a different preference between both types of cars and would choose based on some of the factors underlined here.
The important thing is to go from Point A to Point B. Cheers!

