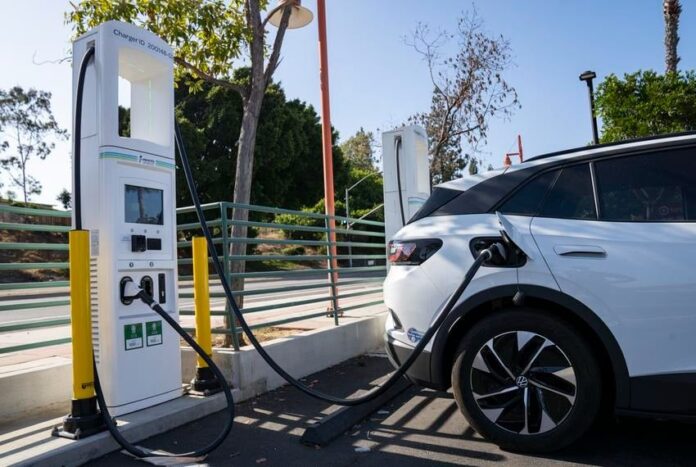
The auto industry is changing because of electric automobiles for various reasons. Manufacturers, regulators, governments, the general public, and stakeholders are calling for accountability in the manufacturing of vehicles due to the need for proactive action to safeguard our environment and reduce global emissions. The manufacture of electric cars also known as EVs (Electric Vehicles) has increased due to the ripples this has created in the automobile sector.
Even though locating an electric automobile in some countries is like looking for a needle in a haystack, electric vehicles clearly outperform internal combustion engines in many ways.
You should be aware that electric vehicles lack the traditional internal combustion engine in favor of an electric motor in order to comprehend how they operate. The huge traction battery that powers the car must be charged by plugging it into an electrical outlet, either at charging stations or wall outlets.
Electric cars are the vehicles of the future.
This type of car does not generate toxic gases through exhaust systems and does not have a liquid fuel system because it is powered by electricity. The battery stores the electricity, which is then utilized to power the electric motor, which in turn powers the wheels and other components of the vehicle. When the batteries’ internal energy reserves run out, charging stations or wall plugs on the grid are used to recharge. Because they are entirely powered by electricity and do not require gasoline or diesel engines as backup, these vehicles are referred to as all-electric vehicles.
In contrast to vehicles powered by internal combustion engines, battery electric vehicles do not emit carbon monoxide, unburned hydrocarbons, or nitrogen oxide; however, the electricity they use during the extraction of fuels, as well as during its generation and distribution, does produce heat-trapping gases and other types of emissions. The method used to generate electricity affects how much pollution there is.
Electric vehicles are a more environmentally friendly option because, for example, in America, charging batteries using energy produced from coal fuels results in less pollution and has less of a negative impact on the environment than gasoline-powered engines.
Battery-powered electric cars are far less expensive to maintain than regular autos.
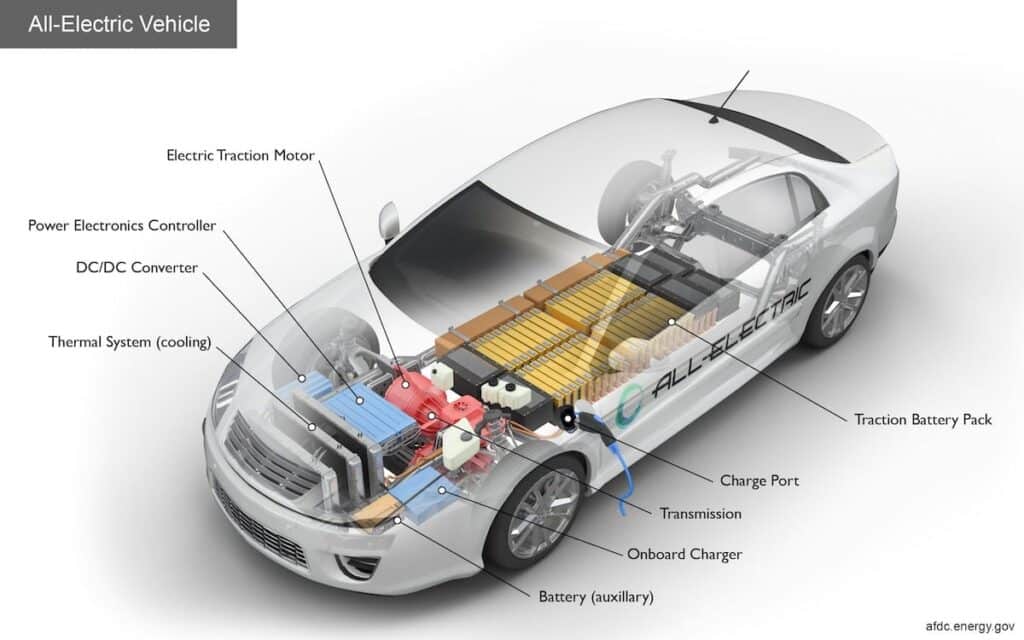
Key components of the electric car
The following key components account for how electric cars work:
Photo credit: afdc energy.gov
- Battery
The electric motors receive power from the controllers, which are then powered by this. Direct current is generated by the lithium cells that make up the device.
- Charge port
This is where the electric car connects to the house outlets and charging stations that are used to recharge the electric traction batteries.
- Inverter
Electric motors are slowed down by inverters, which change direct current to alternating current.
- Drivetrain
To enable mobility, the motor sends power through this one-speed gearbox to the wheels.
- DC/DC converter
In order to operate the vehicle systems and recharge the auxiliary batteries, higher voltage DC power from the traction battery packs is converted in this way to lower voltage DC power.
- Electric traction motors
This serves as the driver of the wheels using power from the batteries.
- Onboard charger
In order to charge traction batteries, the alternate current from the charging station is converted into direct current electricity using this. It keeps track of the battery’s parameters during charging, including voltage, current, temperature, and charge level.
- Power electronics controller
By regulating the torque of electric traction motors, this device regulates the quantity of electricity given to the wheels.
- Thermal cooling system
This gadget guards against overheating and makes sure that all systems and components are operating at the right temperature.
- Traction battery pack
This battery stores electricity to be consumed by the traction motor.
- Transmission
By doing so, mechanical energy is transmitted to power the wheels. The electric traction motors are what produce and transmit the power.
How it works
Electric vehicles change direct current, or current flowing in one direction, into alternating current, or current that changes direction.
Compared to internal combustion engines, electric cars are easier to comprehend in terms of how they operate. Because the electric system does not resemble a plumbing system, maintenance downtime is reduced.
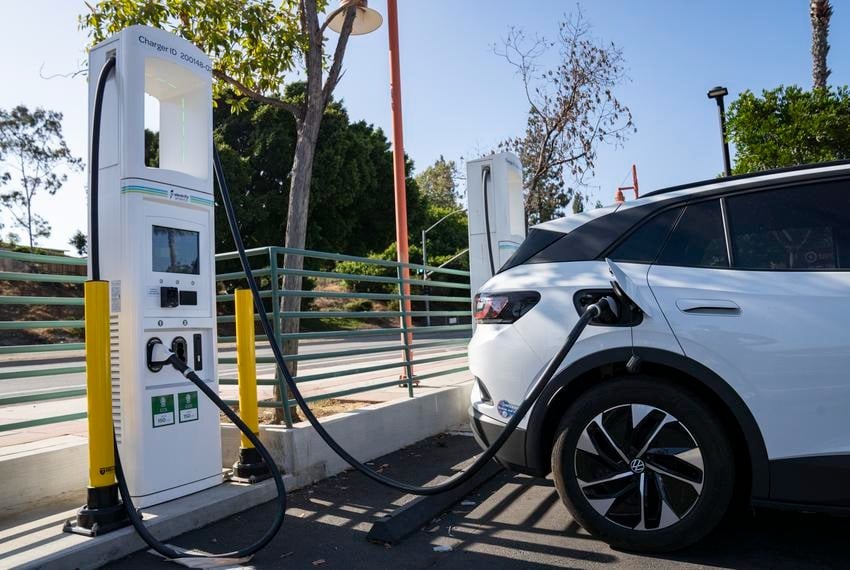

Electric cars can be recharged at home or at charging points in public.
Typically, it has an ac motor installed for mechanical power generating. It does not come equipped with cylinder heads, fuel systems, inlet or exhaust valves, or any of those.
Electricity from the car’s battery packs powers the motor. This provides the energy needed to power various systems, components, and accessories. Depending on the input from the accelerator pedal, the controller regulates the flow of electricity and the power to the electric motor.
Both public and residential outlets can be used to plug in the rechargeable batteries. High-voltage electricity is provided by public charging stations, which reduces the charging time to one or two hours. An electric automobile may need more than ten hours to complete a full charge using standard home outlets.
Pros of the electric car
- EVs reduce emissions as they are 100% eco-friendly. By owning an electric car, you will be playing a vital role in protecting the climate and environment.
- Electric cars are cost-effective; the cost of recharging depleted batteries is low, thereby saving you money.
- Electric cars outperform conventional internal combustion engine vehicles in terms of responsiveness and torque.
- Electric cars reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources for fuel.
- The reduction in parts and systems that do not require constant lubrication reduces the onset of wear, tear and maintenance.
- Smooth-running electric cars produce minimal noise in comparison with their ICE (internal combustion engine) counterparts.

Tesla is a big name in the electric car manufacturing industry
Cons of the electric car
- Recharging points are not widely available yet. We are still in the formative stages of ensuring every nook and cranny is equipped with one. This means that if you travel far away from your local charging point, you may be stuck if that area has yet to have a charging point.
- Electric cars consume electricity, which is not free. In terms of emissions, producing and generating electricity releases negative emissions into the environment.
- While it takes minutes to replenish the fuel in your conventional gasoline-powered vehicle, with electric cars, it takes considerably longer.


