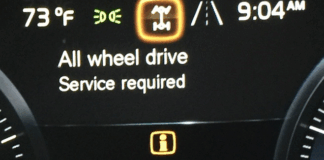
Seeing the “AWD System Malfunction: 2WD Mode Engaged” alert flash on your Toyota’s dashboard can be unsettling. Your vehicle’s all-wheel drive has shifted to front-wheel drive, leaving you curious about the cause and the severity of the issue. Fortunately, many triggers are less complicated than they seem, and some fixes are budget-friendly.
What Does This Alert Signify?
Toyota’s AWD systems are engineered to dynamically allocate power to all four wheels depending on road conditions. If an issue is detected, the system defaults to 2WD mode to safeguard itself.
This alert signals that your AWD system has encountered a glitch and has switched to 2WD (usually front-wheel drive) operation. You can still operate the vehicle, but you’ll lack the enhanced grip of all-wheel drive until the issue is fixed.
Frequent Triggers of Toyota AWD Malfunctions
Battery and Electrical Problems
Issues with the battery are a surprisingly common reason for AWD system failures. Your Toyota’s AWD components need steady voltage to operate correctly.
A low or failing battery can prompt this alert because the system’s sensors and actuators require consistent voltage (ideally 12.6V or more). If voltage dips below 12V, fault codes may appear, disabling AWD functionality.
Basic checks you can do:
- Check battery terminals for signs of corrosion
- Test battery voltage (should exceed 12.4V with the engine off)
- Ensure connections are secure
In many instances, simply charging a drained battery can fully resolve the issue, as one 2017 RAV4 owner found.
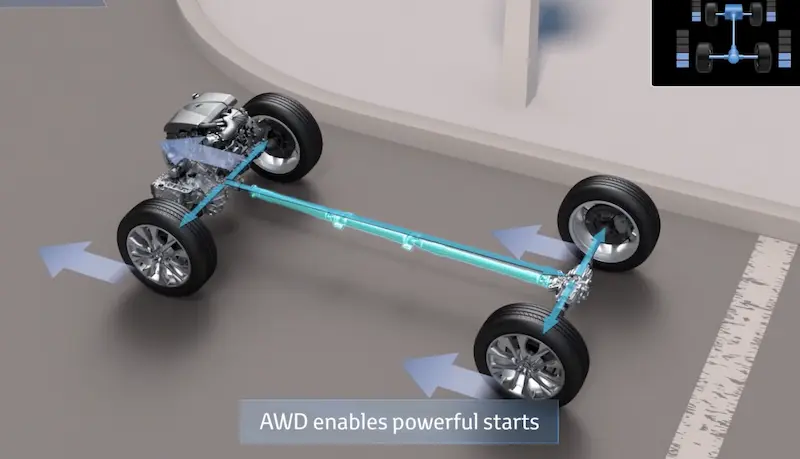

Sensor Malfunctions
Contemporary AWD systems depend on multiple sensors to work properly. When these sensors fail, the system shifts to a fail-safe mode.
Wheel Speed Sensors
Every wheel has a sensor tracking its rotation speed. The AWD system relies on this data to distribute torque effectively. If these sensors malfunction, the system struggles to gauge wheel speeds and reverts to 2WD.
Typical wheel speed sensor problems include:
- Damage to sensors or their wiring
- Debris contamination from roads
- Internal electrical faults
- Damaged wires or connectors
Transmission Range Sensor Issues
The transmission range sensor informs the vehicle of the selected gear. A faulty sensor might incorrectly indicate that the car is in neutral or park while moving, disrupting the AWD system and causing it to deactivate.
This problem often coincides with transmission issues like shifting difficulties or unpredictable gear changes.
Engine-Related Problems
Surprisingly, issues unrelated to the drivetrain can also cause AWD malfunctions.
Check Engine Light Link
Were you aware that your Toyota disables AWD when the check engine light activates? This occurs even for minor issues like a loose fuel cap or a defective oxygen sensor.
A 2018 RAV4 owner posted on Reddit that securing their fuel cap resolved their AWD warning by fixing an evaporative emissions leak that triggered the check engine light.
If the check engine light appears alongside the AWD alert, resolving the engine issue first may fix both.
Mechanical Issues and Overheating
Occasionally, the problem is mechanical rather than electrical.
Overheated AWD Parts
Harsh driving conditions, such as towing heavy loads, spirited driving, or operating in extreme heat, can overheat the AWD system. Toyota’s system has a thermal protection mode that switches to 2WD to avoid damage.
Indicators of overheating AWD components include:
- Grinding or clunking sounds
- Warning appearing after prolonged driving
- Problems during towing or steep inclines
A Toyota Technical Service Bulletin for 2019-2020 RAV4 models addresses overheating issues causing noise and AWD malfunctions.
Low Differential or Transfer Case Fluid
Insufficient lubrication in AWD components can lead to increased friction, heat buildup, and eventual system failure. Toyota specifies particular fluid types and maintenance schedules for differentials.
Diagnosing Your Toyota AWD Issue
Simple DIY Inspections
Before visiting a mechanic, try these straightforward checks:

- Test the battery: Check voltage and examine terminals
- Look for visible damage: Inspect for obvious wiring or fluid leaks
- Scan for fault codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to identify specific errors
- Reset the system: Disconnecting the battery for 15 minutes can sometimes clear temporary errors
Typical Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Scanning your vehicle may reveal these AWD-related codes:
| Code | Description | Potential Fix |
|---|---|---|
| C0215 | Rear Speed Sensor Circuit Issue | Replace wheel speed sensor |
| P0705 | Transmission Range Sensor Error | Adjust or replace sensor |
| P0456 | Evaporative Emissions Leak | Secure gas cap, inspect EVAP system |
When to Seek Professional Help
While simple checks may fix minor issues, some problems need professional diagnostics with advanced tools. A technician can:
- Use Toyota’s Techstream software for detailed analysis
- Test sensors and actuators individually
- Monitor live AWD system data
- Check for AWD-related software updates
Resolving Toyota AWD Issues
Easy Fixes to Attempt
- Battery reset: Disconnect the negative terminal for 15 minutes, then reconnect to clear minor electronic issues.
- Fix check engine light issues: If the check engine light is on, address those problems first. A simple fix like tightening the gas cap may resolve both alerts.
- Check fluid levels: Verify transfer case and differential fluid levels if you’re confident doing so.
Professional Repairs and Costs
For more intricate problems, professional repairs may be required. Here’s an estimated cost breakdown:
| Component | Parts Cost | Labor Cost | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheel Speed Sensor | $80-$150 | $100-$200 | $180-$350 |
| Transmission Range Sensor | $120-$300 | $150-$250 | $270-$550 |
| Battery Replacement | $150-$300 | $20-$50 | $170-$350 |
| Transfer Case Assembly | $2,000-$4,500 | $500-$1,000 | $2,500-$5,500 |
| Transfer Case Assembly | $2,000-$4,500 | $500-$1,000 | $2,500 Supported by the wp-block-table”> |
Toyota service centers can also perform ECU reprogramming to fix software-related issues, especially crucial for newer models with advanced AWD systems.
Preventing AWD System Failures
Consistent maintenance greatly lowers the chances of AWD system issues:
Battery Maintenance
- Regularly test your battery, especially before cold seasons
- Ensure terminals are clean and connections are secure
- Replace batteries older than 4-5 years, even if they appear functional
Fluid Maintenance
Adhering to Toyota’s recommended maintenance schedule for differential and transfer case fluid changes helps avoid mechanical failures. These are often neglected tasks that can lead to costly repairs if ignored.
Early Signs to Monitor
Be alert for these early signs of potential AWD problems:
- Strange noises when turning
- Vibrations during acceleration
- Hesitation on slippery surfaces
- Difficulty accelerating from a standstill
Tackling these symptoms promptly can prevent more severe issues.
Driving Safely With an AWD Issue
If you’re dealing with the “AWD System Malfunction: 2WD Mode Engaged” alert and can’t address it immediately, adjust your driving habits:
Temporary Driving Changes
- Avoid off-road driving or severe weather conditions if feasible
- Take corners cautiously, especially in wet conditions
- Allow extra stopping distance on slick roads
- Prevent aggressive acceleration to avoid wheel spin
While 2WD mode is safe for regular driving, you’ll need to exercise caution in scenarios where AWD traction is typically beneficial.
When to Halt Driving
Though most AWD issues won’t stop you from reaching your destination, cease driving immediately if:
- You hear grinding or loud mechanical sounds
- The vehicle behaves erratically or unpredictably
- Multiple dashboard warning lights appear
- You detect burning smells from the drivetrain
Toyota Models Prone to Issues
This AWD malfunction can impact any Toyota with all-wheel drive, but it’s especially prevalent in:
- RAV4 (notably 2019-2020 models)
- Highlander
- Venza
- 4Runner with part-time 4WD systems
- Sienna AWD models
Each model employs slightly different AWD technology, but the warning messages and many causes are consistent across Toyota’s lineup.
Evolution of Toyota AWD Systems
Toyota has steadily advanced its AWD technology over time:
- Older RAV4 models used a basic AWD system that activated rear wheels upon detecting front wheel slip
- Recent models feature Dynamic Torque Vectoring AWD, directing power to specific wheels as needed
- Hybrid models employ a unique system with an electric motor powering the rear wheels
This progression means diagnostic and repair methods may vary depending on your model and year.
Conclusion
Encountering the “Toyota AWD System Malfunction: 2WD Mode Engaged” alert can be worrisome, but it’s often fixable with simple solutions. From battery problems to sensor replacements, most cases don’t demand major repairs.
By understanding common triggers and following the diagnostic steps provided, you can tackle this issue systematically and restore your Toyota’s AWD functionality. Keep in mind that driving in 2WD mode is generally safe for normal conditions while you arrange for proper diagnosis and repair.