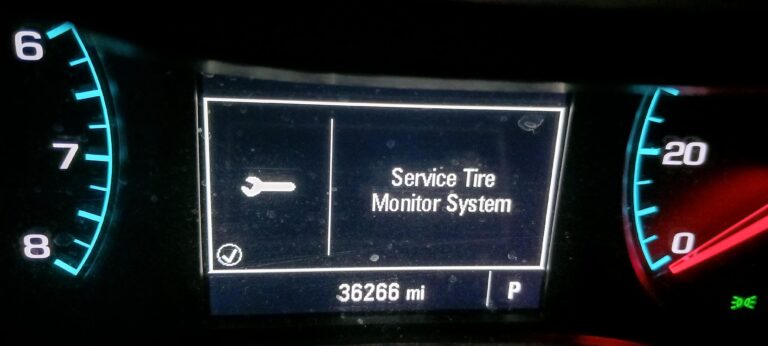
Encountering the “Service Tire Monitor System” message on your GMC vehicle can feel overwhelming, but it’s a helpful reminder about maintaining your tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS). This alert often signifies an issue such as low tire pressure, a malfunctioning sensor, or a depleted sensor battery. Addressing this promptly ensures safer driving and optimal vehicle performance. Read on to discover practical solutions and tips to resolve this issue effectively.
Understanding GMC’s Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
GMC’s Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is designed to enhance road safety by continuously monitoring tire pressure and notifying drivers of potential issues. This system plays a crucial role in preventing tire-related accidents and maintaining your vehicle’s overall efficiency.
What is TPMS and How Does it Work?
The TPMS uses sensors within each tire to measure air pressure and relay the data to your vehicle’s dashboard. If the pressure falls below the recommended level, a warning light illuminates, prompting immediate action. This ensures that drivers are aware of their tires’ condition and can address any issues promptly to avoid more significant problems, such as blowouts or uneven tread wear.
Maintaining the correct tire pressure is critical, not only for safety but also for achieving optimal fuel efficiency. Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, leading to smoother handling and better gas mileage, ultimately saving you money over time.
Key Components of the TPMS
The TPMS is composed of several essential parts. At the heart of the system are tire pressure sensors installed in each wheel. These sensors detect pressure changes and send data to the vehicle’s central monitoring unit. The control module processes this information and displays alerts on the dashboard when necessary.
Additionally, some advanced GMC models feature wireless communication systems for real-time monitoring. Each component works together to provide timely updates, ensuring you stay informed about your tires’ condition while driving.
Fuel Efficiency Benefits of TPMS
One often-overlooked benefit of a functioning TPMS is its positive impact on fuel efficiency. When tires are inflated to the recommended pressure, your vehicle experiences less rolling resistance, which translates to improved fuel economy. Over time, this can result in significant cost savings at the pump.
By regularly monitoring TPMS alerts and maintaining proper tire pressure, you not only extend the life of your tires but also contribute to a greener, more environmentally friendly driving experience.
Decoding the ‘Service Tire Monitor System’ Message
Seeing the “Service Tire Monitor System” message can be alarming, but understanding its cause is the first step to resolving it. This alert serves as a prompt to address potential TPMS issues and ensure your vehicle remains in peak condition.
What Does the Warning Signify?
This warning typically indicates a malfunction within the TPMS. Common causes include low tire pressure, sensor failure, or a depleted sensor battery. It may also result from calibration errors or issues stemming from recent tire maintenance.
For example, in GMC models like the Acadia, this message might appear if the sensors detect abnormal pressure levels or fail to communicate with the system. Resolving the issue promptly minimizes risks associated with driving on underinflated or overinflated tires.
Common Triggers for the Alert
Low tire pressure is one of the primary reasons for this warning. Tires naturally lose air over time, especially during temperature fluctuations. Regularly checking and inflating your tires can help prevent this issue.
Another frequent cause is a malfunctioning TPMS sensor. These sensors have a finite lifespan and may need replacement after several years. Additionally, improper sensor calibration following tire rotations or replacements can trigger the message. Ensuring proper installation and programming is crucial to avoid unnecessary alerts.
Troubleshooting GMC TPMS Issues
Addressing TPMS problems requires a combination of resetting the system, using diagnostic tools, and identifying underlying faults. Understanding these steps can help you maintain the reliability of your tire monitoring system.
Resetting the TPMS
To reset the TPMS, begin by inflating all tires to their recommended pressure levels. Start your vehicle and allow it to run for a few minutes to see if the warning light turns off. If the light remains on, driving at a steady speed above 50 mph for about 10 minutes can help recalibrate the system automatically.
For more persistent issues, consult your GMC manual for specific reset procedures. In some cases, manually resetting the system using a TPMS reset button or through the vehicle’s infotainment system may be necessary.
Using a TPMS Diagnostic Tool
A TPMS diagnostic tool can help pinpoint issues when a reset doesn’t resolve the problem. These tools detect sensor signals, confirm functionality, and identify specific malfunctions such as weak sensor batteries or signal interference.
They are particularly useful after installing new sensors or rotating tires. A diagnostic tool ensures all sensors are communicating correctly, reducing the likelihood of false alerts.
Addressing Common TPMS Issues
Frequent TPMS faults include dead sensor batteries and incorrect tire pressure readings. If the warning persists despite proper inflation, sensor replacement may be required. Faulty wiring or outdated software can also contribute to persistent alerts.
To prevent these problems, schedule routine inspections with a qualified technician. Addressing minor faults early can save you from more extensive and costly repairs in the future.
Leveraging an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is a powerful tool for diagnosing advanced TPMS issues. It retrieves error codes that can identify specific faults within the system, such as sensor malfunctions or communication errors.
Using an OBD-II scanner allows you to clear fault codes after resolving issues, ensuring the system functions correctly. This tool is especially valuable for persistent problems that cannot be fixed with standard resets or manual inspections.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Maintaining proper tire pressure and adhering to routine maintenance schedules are vital for the longevity of your tires and the overall safety of your vehicle.
Manually Checking Tire Pressure
To manually check your tire pressure, use a reliable pressure gauge. Remove the valve cap, press the gauge onto the valve stem, and note the PSI reading. Compare it to the recommended levels listed in your vehicle’s manual or on the driver’s door jamb.
Frequent pressure checks—at least once a month—help ensure consistent performance, reduce the risk of uneven wear, and improve fuel efficiency. This simple practice can prevent many TPMS alerts and prolong tire life.
Tire Rotation and Load Information
Rotating your tires at regular intervals promotes even tread wear and extends tire lifespan. Follow the rotation schedule outlined in your GMC manual, typically every 5,000 to 8,000 miles.
Additionally, refer to the tire and loading information label for details about recommended pressures and load capacities. Proper adherence to these guidelines enhances both safety and vehicle performance.