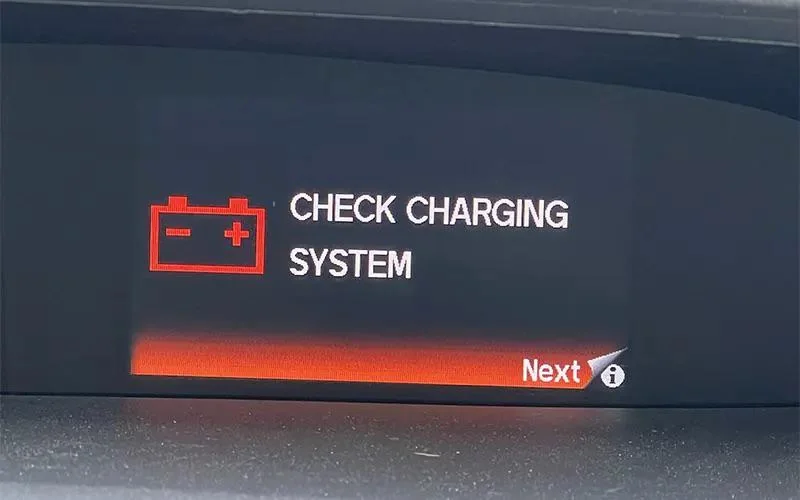
A malfunctioning ECU, a defective alternator, or an aging battery can disrupt your vehicle’s charging system. Ignoring these issues can lead to further damage, as a faulty alternator or improper voltage regulation can harm the battery.
What Triggers the Check Charging System Warning?
The “Check Charging System” warning light on your dashboard signals potential problems with the vehicle’s charging system. Below are the three primary causes of this issue and how to address them.
Defective Alternator – A malfunctioning alternator fails to deliver stable voltage to the battery. If the voltage output is too high or too low, it can damage the battery and other components of the charging system.
Signs of a failing alternator include dim or flickering cabin lights or other electrical malfunctions in the vehicle.
A professional mechanic can repair a faulty alternator, but costs can vary. In severe cases, replacing an alternator may exceed $1,000, depending on the extent of the damage.
ECU Malfunction – The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) manages various electrical systems in your vehicle. If it malfunctions, the alternator may not function properly, causing the charging system to fail.
Improperly jump-starting a vehicle is a common cause of ECU damage. Resetting the ECU may resolve minor issues, but a severely damaged ECU will require replacement.
Aging or Damaged Battery – Batteries naturally degrade over time and may struggle to hold a charge. Physical damage, such as from a collision, can also impair the battery’s performance.
Replacing a battery is often more cost-effective than repairing it. For Honda vehicles, a new battery typically costs between $50 and $400, depending on the model.
What Is a Vehicle Charging System?
All vehicles rely on a battery to power essential components, with some, like hybrids, using batteries to assist in propulsion.
In hybrid vehicles, the battery serves as an additional power source. However, no vehicle battery is self-sustaining; it requires a charging system to maintain its charge.
Without a functional charging system, the battery will deplete, rendering it ineffective and unable to power systems like the radio, air conditioning, or lights.
The charging system ensures the battery remains charged and supports the vehicle’s electrical demands.
Typically, a charging system includes a battery, wiring, an ECU, and an alternator. High-performance vehicles, such as race cars, may incorporate additional components.
How to Reset Your Honda’s Charging System
Before visiting a mechanic, you can attempt to reset the charging system yourself. Resetting a Honda’s charging system is straightforward.
To reset, turn off the vehicle, open the hood, and secure it properly to prevent it from closing unexpectedly.
Locate the battery and identify the wire connecting it to the engine.
Disconnect the battery from the engine, wait for 30 seconds, then reconnect the wire. Start the vehicle. If the “Check Charging System” warning no longer appears, the issue is resolved.
If the warning persists, try resetting the ECU, which controls the vehicle’s computer, sensors, and actuators.
In some vehicles, the ECU is referred to as the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) if it manages the engine and transmission.
Steps to Reset the ECU
Begin by turning off your Honda and opening the hood, ensuring it is securely propped open.
Locate the fuse box, which typically includes a diagram on its cover indicating which fuse corresponds to each component.
Find the fuse labeled “ECU” on the diagram. Remove the cover and carefully extract the ECU fuse.
Inspect the fuse for any signs of damage. If it’s intact, reinsert it after waiting 30 seconds. If damaged, replace it with a new fuse.
Close the fuse box and hood, then start the vehicle. The warning light should no longer appear on the dashboard.
If the warning persists, the issue is likely not a simple glitch, and a visit to a mechanic is necessary.
Checking Your Honda’s Battery Charge
Measuring your battery’s charge is simple with the right equipment. You’ll need a digital voltmeter.
Attach the voltmeter’s positive lead to the battery’s positive terminal and the negative lead to the negative terminal.
The voltmeter will display the battery’s voltage immediately. A healthy Honda battery should typically register at least 12.4 volts, though exact specifications vary by model.
Final Thoughts
A properly functioning vehicle battery should maintain a voltage of 12.4 volts or higher. If you suspect an ECU issue, try resetting it before seeking professional help.
You can also verify your Honda’s battery charge using a digital voltmeter. Common charging system issues include worn-out batteries and malfunctioning alternators, which trigger the “Check Charging System” warning on the dashboard.
The core components of the charging system are the battery, wiring, ECU, and alternator, all working together to keep your vehicle powered.